
| THE HEX SERIES |
Thin films are an inseparable part of modern technology. When deposited on the surface of an object, thin film coatings can alter its qualities, for example, increasing durability, changing electric conductivity, or improving optical properties.
But how do we define a ‘thin film’? A thin film is a layer of material ranging in thickness from sub-nanometers to microns. Thin film deposition techniques fall under the broad categories of physical vapour deposition and chemical vapour deposition.
The history of thin solid films begins in antiquity [1], with metallic films (usually gold platings) used on various artefacts for decorative and protective purposes. Today, many industries rely on precise atomic layer deposition to produce high-purity thin films.
Industrial applications include thin film solar cells, optical lenses with a high refractive index, anti-reflective optical coatings, semiconductor devices, light crystal displays, and more.
In this article, you’ll find out more about thin films and the thin film deposition process.
What is Thin Film Deposition?
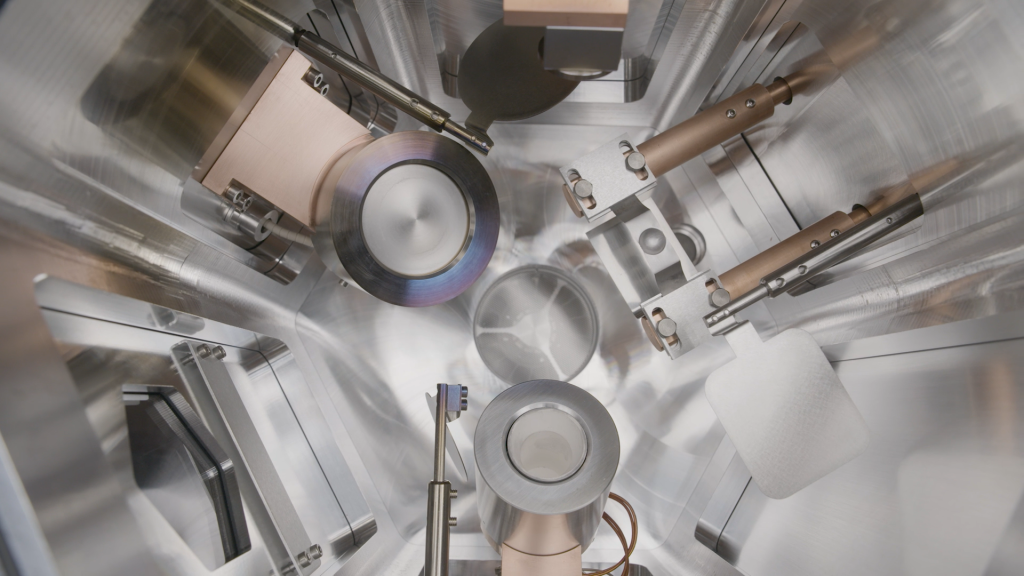

The thin film deposition process may vary depending on the techniques used, but all the methods we discuss involve placing a thin layer of deposited film on the substrate surface within a vacuum chamber.
The first creation of metal films by chemical vapour deposition took place in the mid-17th century. Experiments in oxide deposition began circa 1760, while sputter deposition took its first steps in the 1850s [2].
By the 1930s, manufacturers already used early-stage thin films for high-reflectivity mirrors. The 1960s technologies of ultra-high vacuum and in situ electron microscopy enabled the creation of more advanced, pure, and uniform thin films. In 1970, Peter J. Clarke launched the first sputter gun that created atomic-scale films by using ion and electron collisions.
Advanced technologies, such as atomic resolution surface imaging, allowed the progress of the thin film industry as we know it today. Methods for depositing thin films, such as sputtering-based methods, continue to grow and develop into new applications.
Physical vapour deposition (PVD), which involves the vaporisation and depositing of solid material on a substrate, encompasses a range of methods from a basic evaporation process to magnetron sputtering and pulsed laser deposition [3].
Many advanced thin-film devices, like the HEX Series by Korvus Technology, use physical deposition methods. PVD, in particular sputtering systems, allow manufacturers to create highly precise and uniform thin films.
In contrast, chemical vapour deposition relies on a reaction between precursors in the deposition chamber. CVD has several common uses, like creating Si thin films. One drawback of CVD is the need for extra-high temperatures to incite the process.
The Different Thin Film Deposition Techniques: Physical Vapour Deposition and Chemical Vapour Deposition
Deposition techniques fall into two main groups: physical vapour deposition and chemical deposition. Physical Vapour Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD) differ fundamentally in their deposition methods. PVD involves the physical transfer of materials under vacuum, where vaporised materials condense onto the substrate, making it ideal for metals and alloys. In contrast, CVD utilises chemical reactions at elevated temperatures to deposit materials from a vapour phase, suitable for complex compounds and polymers. PVD offers precise control over thickness and purity, whereas CVD excels in achieving uniform coatings over intricate shapes. The choice between PVD and CVD depends on the required material properties and the specific demands of the application.
See more: PVD vs CVD
Physical Vapour Deposition Methods
There are a wide range of thin film deposition techniques and choosing the best deposition method for you will depend on numerous factors. Things to bear in mind as you make your decision are:
- The target material
- The substrate
- The required deposition rate
- Your application
- Budget available
At Korvus Technology, the HEX Series is a physical vapour deposition coating system, covering a range of techniques which we will explore below.
Thermal Evaporation
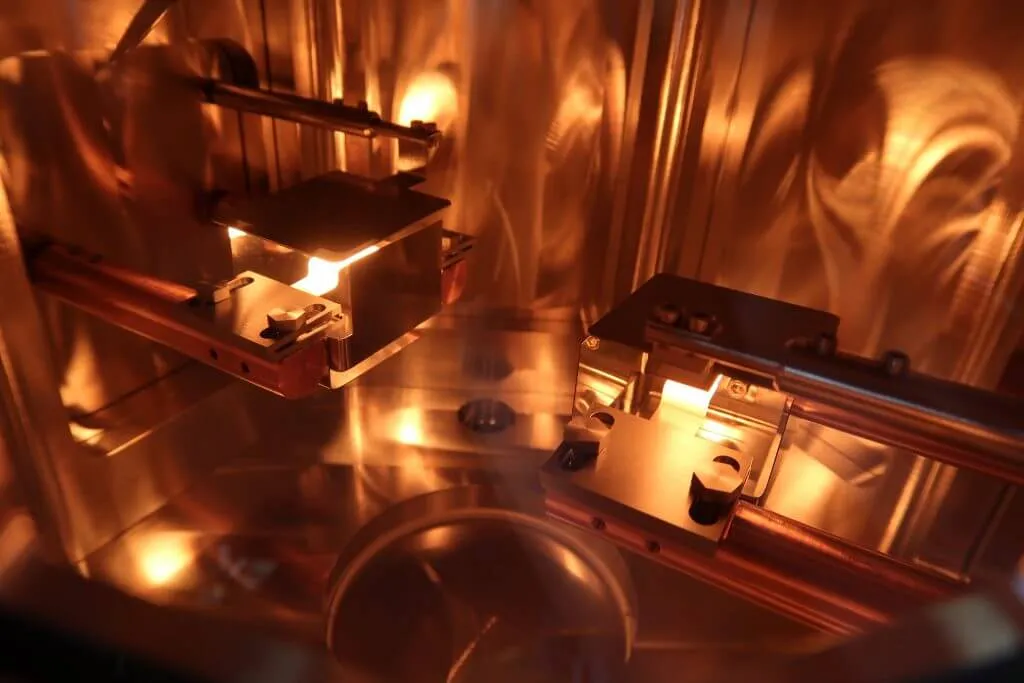

Thermal evaporation deposition occurs in a chamber under the pressure of 10(-6) to 10(-5) mbar. A crucible that connects to a high-current source holds the target material.
Here are the basic steps for thermal evaporation deposition:
- As the surface of the target material heats, it releases vapour particles that create vapour pressure.
- The vapour stream crosses the chamber and coating particles attach to the substrate.
- Throughout the process, the vacuum pump keeps working to maintain a high-vacuum environment and ensure a free path for the film particles.
Magnetron Sputtering
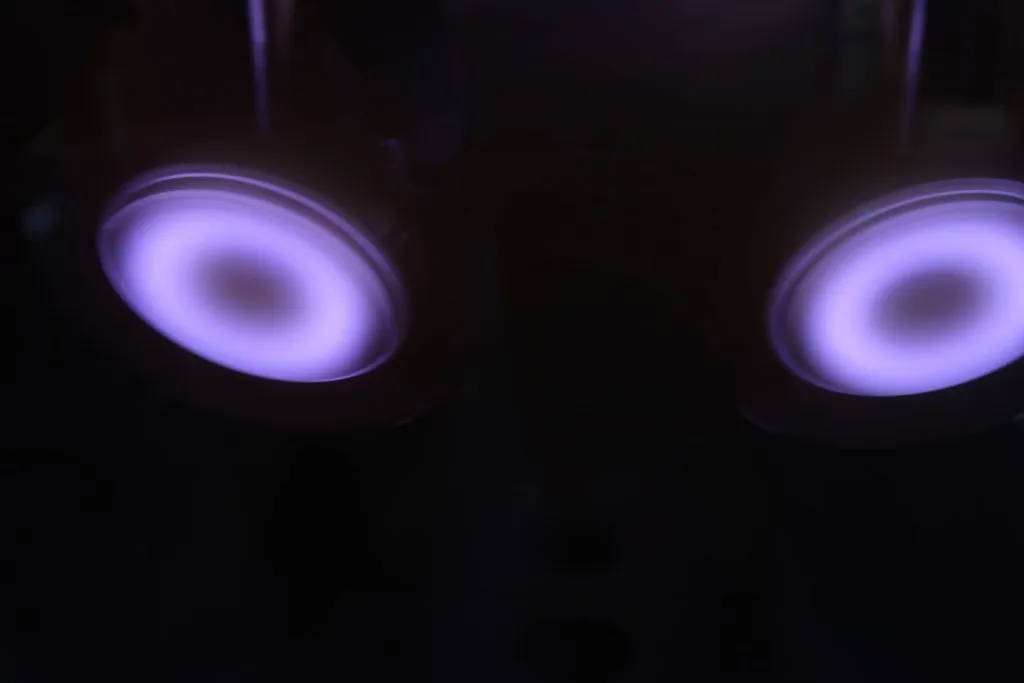

Sputtering is a physical phenomenon leveraged by thin film deposition to expel microscopic particles of solid materials from their surface. This ejection is achieved by attacking the solid material with energetic particles. The particles are then deposited in the target materials forming the thin film layer.
Like other deposition methods, sputtering takes place in a chamber with a vacuum pump constantly working to remove air. The vacuum is a crucial condition for this process, which occurs naturally in outer space.
Magnetron sputtering involves the following steps:
- An inert gas, usually argon, flows continuously into the chamber. Magnet arrays within the cylindrical rotating target generate a magnetic field.
- High voltage creates a gaseous plasma near the target’s magnetic field. The plasma contains argon gas atoms, argon ions, and free electrons. Electrons that hit argon atoms continuously create positively charged ions.
- The negatively charged sputtering target attracts the positively charged ions. As the ions hit the target, they eject atoms.
- The ejected atoms settle on the substrate’s surface and create a film.
Electron Beam Evaporation
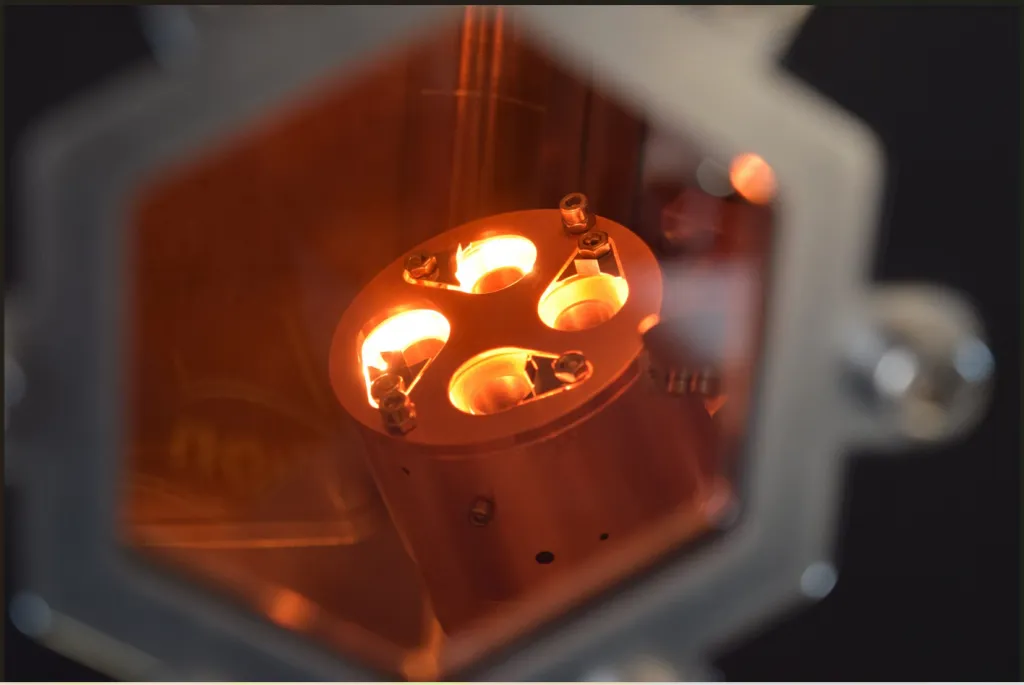
Electron beam evaporation is a process where a focused electron beam vaporises a target material, causing it to condense and deposit material onto a substrate. This technique is preferred over thermal evaporation due to its precise control over the deposition rate and film thickness. It is particularly beneficial for materials with high melting points, ensuring the deposited material maintains purity and quality without substrate contamination. Thus, electron beam evaporation is selected for its superior efficiency and effectiveness in producing high-quality thin films.
Learn More About Electron Beam Evaporation
Organic Evaporation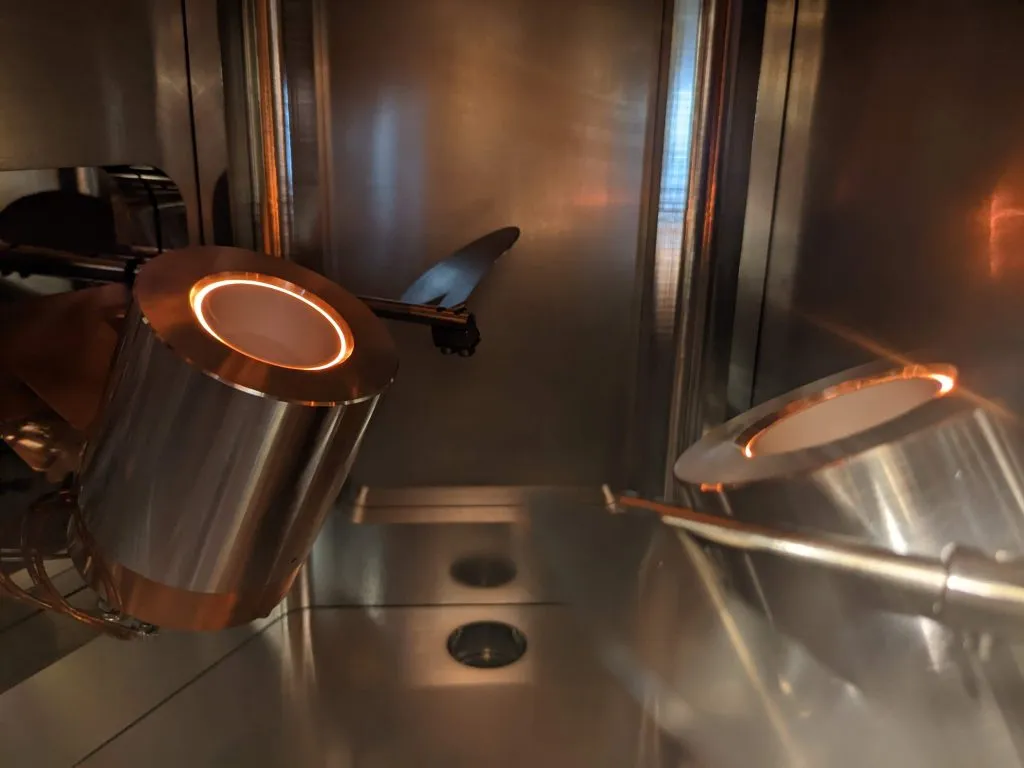
Organic evaporation involves heating organic materials until they vaporise, allowing the material to be deposited onto a substrate. This method is particularly suited for organic compounds that are sensitive to high temperatures or electron beam exposure. Low-temperature evaporation is chosen for its ability to gently deposit thin films of organic materials, such as polymers and organic semiconductors, without altering their chemical structure. It ensures the integrity of the material to be deposited, making it ideal for applications in organic electronics and bio-compatible coatings.
Meet The HEX: A Modular Thin Film Deposition System

The HEX Series offers a flexible array of thin film deposition systems tailored for both research and practical applications. Initially, you can acquire the basic model and progressively enhance it with advanced components based on your desired film thickness, materials and other requirements. This makes it suitable for many applications. These components are designed for easy integration, minimising both the downtime of the system and the cost of installation.
This series is comprised of the compact HEX model and the more spacious HEX-L Systems.
See more:
Thin Film Deposition Technologies: Final Words
The world as we know it today relies on thin films. Thin films are everywhere, from a bag of chips to the device you are using to read this article.
Often invisible, thin films are the quiet superheroes of modern industry, with a range of uses from prolonging shelf life to improving optical properties of lenses. Thin films may consist of metals, oxides, and organic materials.
The technologies for making thin films vary depending on the application and industry demands. If you are interested in learning more about thin films, we invite you to browse other articles at Korvus Technology.
