Dielectric cure monitoring은 풍력 터빈 날개나 합성보와 같은 매우 큰 구조물의 여러 위치에서 복합적인 경화 상태를 측정할 수 있습니다. 본 제품은 항공기나 우주선 부품과 같이 다수의 센서가 필요한 파츠를 측정하는 연장 케이블의 얽힘을 미연에 방지합니다.
본 경화 거동 분석기는 연구, 품질 관리 및 제조 분야에 동일한 센서와 측정을 사용합니다. 본 유전율 분석기(dielectric analyzer)는 시차주사열량계(DSC, differential scanning calorimetry) 또는 동역학 분석기(dynamic mechanical analysis)와 같은 실험실 테스트와 연관성이 있습니다. 결과적으로, 본 기기는 연구소에서 제조 시설, 제조 시설에서 제품 품질 책임자에게 종합적인 경화 거동에 대한 정보를 제공하는 "매개" 역할을 할 수 있습니다.
본 모델은 풍력 터빈 날개와 같은 고가품의 생산성을 즉각적으로 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 보통 50미터가 넘는 이 날개들은 mold로 제작이 됩니다. 날개의 두께와 열 반응성은 제작 길이에 따라 다릅니다. 따라서 경화 속도는 길이에 따라 다르며, 제조 업체는 최적의 demold 시간을 결정하기 위하여 경험과 지식을 필요로 합니다. 경화시간이 충분하지 않다면 날개에는 균열이 발생할 수 있으며, 필요 이상으로 길다면 생산량이 줄어들기 때문입니다.
예를 들어, 유전율 측정 센서를 전략적인 위치나 5미터 간격으로 설치할 경우 어느 시점에 전체적인 영역에서 적절한 경화가 이루어졌는지 알 수 있으며, 최적 공정 시간을 결정할 수 있게 됩니다. 공정 시간이 단축되어 생산성이 향상되면 수익성의 증대를 기대할 수 있습니다.
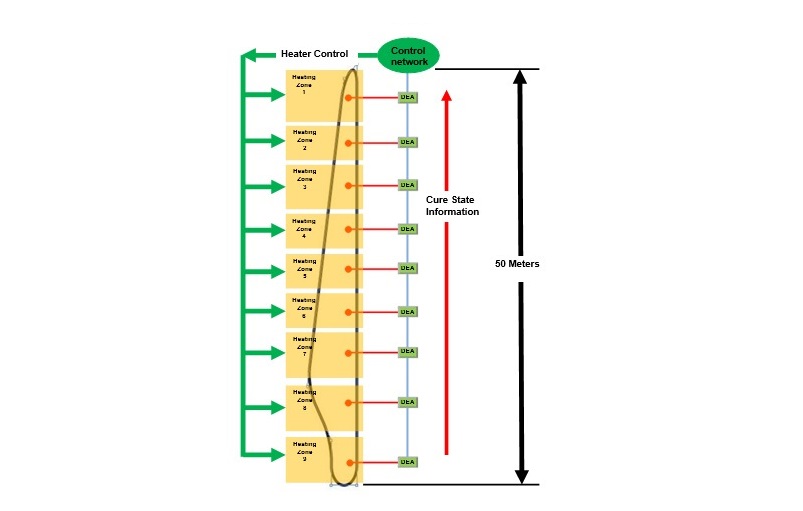
Distributed dielectric cure monitoring allows the measurement of composite cure state at many locations in very large structures such as wind turbine blades and composite beams. Distributed dielectric cure monitoring also avoids the tangle of extension cables used for monitoring parts requiring multiple sensors, such as aircraft and spacecraft components.
Dielectric cure monitoring uses the same sensors and measurements for research, quality control and manufacturing applications. Dielectric Analysis (DEA) correlates with laboratory tests such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) or dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA). As a result, DEA can act as the “go between” that brings information about composite cure from the research lab to the manufacturing floor, and from the manufacturing floor to the manager responsible for product quality.
Dielectric cure monitoring can immediately improve productivity for high value items like wind turbine blades. These blades, often more than 50 meters long, are fabricated in a mold. The thickness of the blade and the exotherm during processing vary along its length. Consequently, the rate of cure also varies along its length, and manufacturers must use experience and guesswork to determine the optimum demold time. Removing a blade too soon can cause cracks because it is not stiff enough, and removing a blade later than necessary reduces throughput.
Dielectric sensors installed in the mold at strategic locations, or perhaps every five meters along its length, for example, can determine when composite cure along the entire part has reached a desired point. Only at that time would the wind turbine blade be removed from its mold. As a benefit, if a factory ships even as little as one or two more blades a week, profitability increases.
Reference :
Lambient TechnologiesTM Technical Overview 3.06—Distributed Cure Monitoring for Wind Blades, Page 6
상세한 사항은 아래 첨부된 자료를 참고 부탁 드립니다.
